所謂的應用層鉤子(Application-level hooks)是一種編程技術,它允許應用程式通過在特定事件發生時執行特定代碼來自定義或擴展其行為,這些事件可以是用戶互動,系統事件,或者其他應用程式內部的事件,應用層鉤子是在應用程式中添加自定義代碼的一種靈活的方式,它們可以用于許多不同的用途,如安全審計、性能監視、訪問控制和行為修改等,應用層鉤子通常在應用程式的運行時被呼叫,可以執行一些預定義的操作或觸發一些自定義代碼,
通常情況下,第三方應用在需要擴展一個程式功能是都會采用掛鉤子的方式實作,而由于記憶體資料被修改后磁盤資料依然是原始資料,這就給掃描這些鉤子提供了便利,具體來說鉤子掃描的原理是通過讀取磁盤中的PE檔案中的反匯編代碼,并與記憶體中的代碼作比較,當兩者發生差異是則可以證明此處被掛了鉤子,
本節內容中,筆者將通過一個案例并配合Capstone引擎來實作這個功能,之所以選用該引擎是因為該引擎支持Python包,可以非常容易的與LyScript插件互動,此外Capstone引擎在逆向工程、漏洞分析、惡意代碼分析等領域有廣泛的應用,著名反匯編除錯器IDA則是使用了該引擎作業的,
-
Capstone引擎的主要特點包括:
-
支持多種指令集:支持x86、ARM、MIPS、PowerPC等多種指令集,且能夠在不同的平臺上運行,
-
輕量級高效:采用C語言撰寫,代碼簡潔高效,反匯編速度快,
-
易于使用:提供了易于使用的API和檔案,支持Python、Ruby、Java等多種編程語言,
-
可定制性:提供了多種可配置選項,能夠滿足不同用戶的需求,
Capstone的安裝非常容易,只需要執行pip install capstone即可完成,使用Capstone反匯編時讀者只需要傳入一個PE檔案路徑,并通過md.disasm(HexCode, 0)即可實作反匯編任務;
代碼首先使用pefile庫讀取PE檔案,獲取檔案的ImageBase,以及名為".text"的節表的VirtualAddress、Misc_VirtualSize和PointerToRawData等資訊,接下來,代碼計算了".text"節表的起始地址StartVA和結束地址StopVA,然后使用檔案指標讀取檔案中".text"節表的原始資料,并使用capstone庫進行反匯編,反匯編結果以字典形式存盤,包括反匯編地址和反匯編指令,最后,函式回傳了包含所有反匯編指令的opcode_list串列,
from capstone import *
import pefile
def Disassembly(FilePath):
opcode_list = []
pe = pefile.PE(FilePath)
ImageBase = pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase
for item in pe.sections:
if str(item.Name.decode('UTF-8').strip(b'\x00'.decode())) == ".text":
# print("虛擬地址: 0x%.8X 虛擬大小: 0x%.8X" %(item.VirtualAddress,item.Misc_VirtualSize))
VirtualAddress = item.VirtualAddress
VirtualSize = item.Misc_VirtualSize
ActualOffset = item.PointerToRawData
StartVA = ImageBase + VirtualAddress
StopVA = ImageBase + VirtualAddress + VirtualSize
with open(FilePath,"rb") as fp:
fp.seek(ActualOffset)
HexCode = fp.read(VirtualSize)
md = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_32)
for item in md.disasm(HexCode, 0):
addr = hex(int(StartVA) + item.address)
dic = {"Addr": str(addr) , "OpCode": item.mnemonic + " " + item.op_str}
print("[+] 反匯編地址: {} 引數: {}".format(addr,dic))
opcode_list.append(dic)
return opcode_list
if __name__ == "__main__":
Disassembly("d://lyshark.exe")
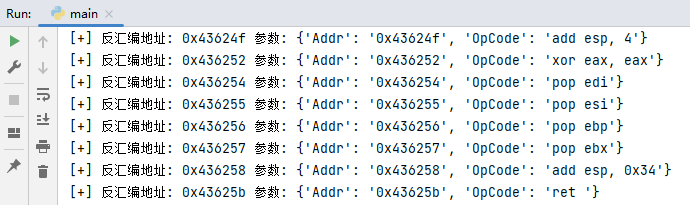
當讀者運行上方代碼片段時,則可輸出lyshark.exe程式內text節所有反匯編代碼片段,輸出效果如下圖所示;
接著我們需要讀入記憶體中的PE檔案機器碼并通過Capstone引擎反匯編為匯編指令集,如下get_memory_disassembly函式則是實作記憶體反匯編的具體實作細節,
此案例中通過read_memory_byte讀入記憶體完整資料,并使用md.disasm依次反匯編,并最終將結果存盤到dasm_memory_dict字典中保存,
import binascii,os,sys
import pefile
from capstone import *
from LyScript32 import MyDebug
# 得到記憶體反匯編代碼
def get_memory_disassembly(address,offset,len):
# 反匯編串列
dasm_memory_dict = []
# 記憶體串列
ref_memory_list = bytearray()
# 讀取資料
for index in range(offset,len):
char = dbg.read_memory_byte(address + index)
ref_memory_list.append(char)
# 執行反匯編
md = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86,CS_MODE_32)
for item in md.disasm(ref_memory_list,0x1):
addr = int(pe_base) + item.address
dasm_memory_dict.append({"address": str(addr), "opcode": item.mnemonic + " " + item.op_str})
return dasm_memory_dict
if __name__ == "__main__":
dbg = MyDebug()
dbg.connect()
pe_base = dbg.get_local_base()
pe_size = dbg.get_local_size()
print("模塊基地址: {}".format(hex(pe_base)))
print("模塊大小: {}".format(hex(pe_size)))
# 得到記憶體反匯編代碼
dasm_memory_list = get_memory_disassembly(pe_base,0,pe_size)
print(dasm_memory_list)
dbg.close()
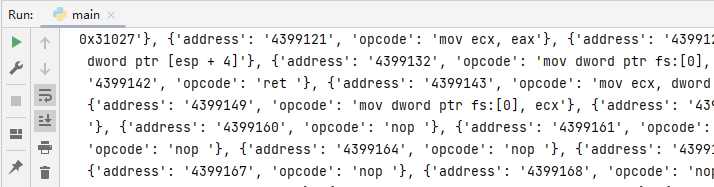
執行如上所示代碼,則可輸出當前程式記憶體中的反匯編指令集,并以字典的方式輸出,效果圖如下所示;
這兩項功能實作之后,那么實作記憶體與磁盤之間的比對作業將變得很容易實作,如下代碼中首先通過get_memory_disassembly獲取到記憶體反匯編指令,然后通過get_file_disassembly獲取磁盤反匯編指令,并將兩者dasm_memory_list[index] != dasm_file_list[index]最比較,以此來判斷特定記憶體是否被掛鉤;
import binascii,os,sys
import pefile
from capstone import *
from LyScript32 import MyDebug
# 得到記憶體反匯編代碼
def get_memory_disassembly(address,offset,len):
# 反匯編串列
dasm_memory_dict = []
# 記憶體串列
ref_memory_list = bytearray()
# 讀取資料
for index in range(offset,len):
char = dbg.read_memory_byte(address + index)
ref_memory_list.append(char)
# 執行反匯編
md = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86,CS_MODE_32)
for item in md.disasm(ref_memory_list,0x1):
addr = int(pe_base) + item.address
dic = {"address": str(addr), "opcode": item.mnemonic + " " + item.op_str}
dasm_memory_dict.append(dic)
return dasm_memory_dict
# 反匯編檔案中的機器碼
def get_file_disassembly(path):
opcode_list = []
pe = pefile.PE(path)
ImageBase = pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase
for item in pe.sections:
if str(item.Name.decode('UTF-8').strip(b'\x00'.decode())) == ".text":
# print("虛擬地址: 0x%.8X 虛擬大小: 0x%.8X" %(item.VirtualAddress,item.Misc_VirtualSize))
VirtualAddress = item.VirtualAddress
VirtualSize = item.Misc_VirtualSize
ActualOffset = item.PointerToRawData
StartVA = ImageBase + VirtualAddress
StopVA = ImageBase + VirtualAddress + VirtualSize
with open(path,"rb") as fp:
fp.seek(ActualOffset)
HexCode = fp.read(VirtualSize)
md = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_32)
for item in md.disasm(HexCode, 0):
addr = hex(int(StartVA) + item.address)
dic = {"address": str(addr) , "opcode": item.mnemonic + " " + item.op_str}
# print("{}".format(dic))
opcode_list.append(dic)
return opcode_list
if __name__ == "__main__":
dbg = MyDebug()
dbg.connect()
pe_base = dbg.get_local_base()
pe_size = dbg.get_local_size()
print("模塊基地址: {}".format(hex(pe_base)))
print("模塊大小: {}".format(hex(pe_size)))
# 得到記憶體反匯編代碼
dasm_memory_list = get_memory_disassembly(pe_base,0,pe_size)
dasm_file_list = get_file_disassembly("d://lyshark.exe")
# 回圈對比記憶體與檔案中的機器碼
for index in range(0,len(dasm_file_list)):
if dasm_memory_list[index] != dasm_file_list[index]:
print("地址: {:8} --> 記憶體反匯編: {:32} --> 磁盤反匯編: {:32}".
format(dasm_memory_list[index].get("address"),dasm_memory_list[index].get("opcode"),dasm_file_list[index].get("opcode")))
dbg.close()
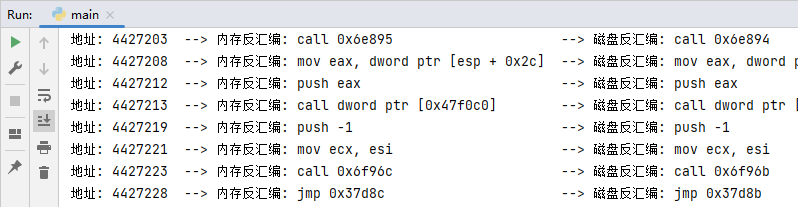
運行上方代碼片段,耐性等待一段時間,則可輸出記憶體與磁盤反匯編指令集串列,輸出效果圖如下所示;
原文地址
https://www.lyshark.com/post/ccb35246.html
文章作者:lyshark (王瑞)文章出處:https://www.cnblogs.com/LyShark/p/17539915.html
本博客所有文章除特別宣告外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 許可協議,轉載請注明出處!
轉載請註明出處,本文鏈接:https://www.uj5u.com/qiye/556964.html
標籤:其他
上一篇:ENVI實作QUAC、簡化黑暗像元、FLAASH方法的遙感影像大氣校正
下一篇:返回列表
